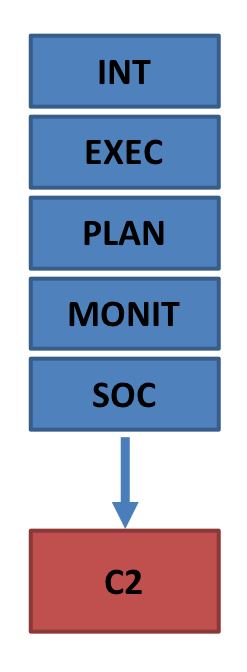
To assess the reliability of the first coder's coding, the following four high inference attributes were double coded by second coders.
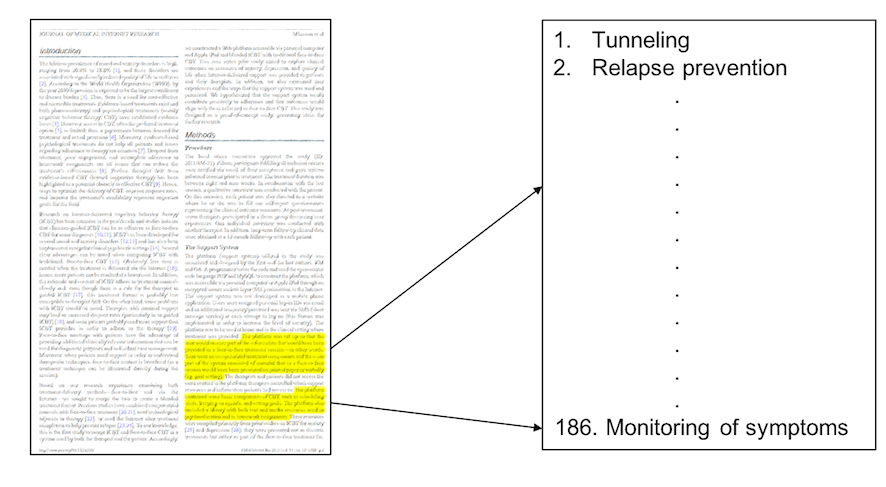
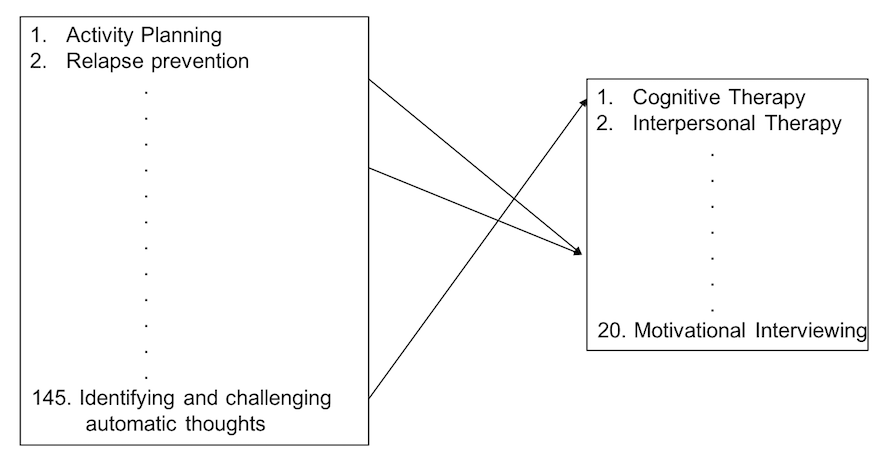
The task entailed that a second coder identifies functions within a system description. System descriptions are provided in the original literature. A total of 186 possible functions could be identified.

When classifying functions, the second coder was provided with snippets of text that had been identified as functions by the first coder. These snippets were taken directly from the literature. The task of the second coder was to identify from the list of 186 possible functions, which one the snippet descibed.
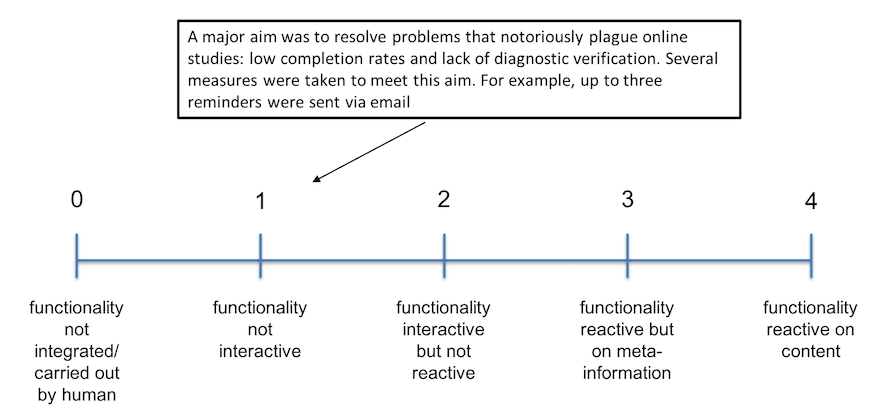
Here second coders assigned a rating of technological sophistication to a snippet of text descibing the implementation of a function. Each coder only coded functions of a specific function type (intervention, planning support, execution support, monitoring support, or social support), and therefore also only had to work with one scale.
A graduate student in clinical psychology double-coded the mapping between intervention functions at the lowest level and their corresponding therapeutic frameworks.
Two types of validation analyses were conducted. One, we examined how well the five scales captured people's intuitive notion of the concept of technological sophistication. Two, we examined how comparable the five different scales were.
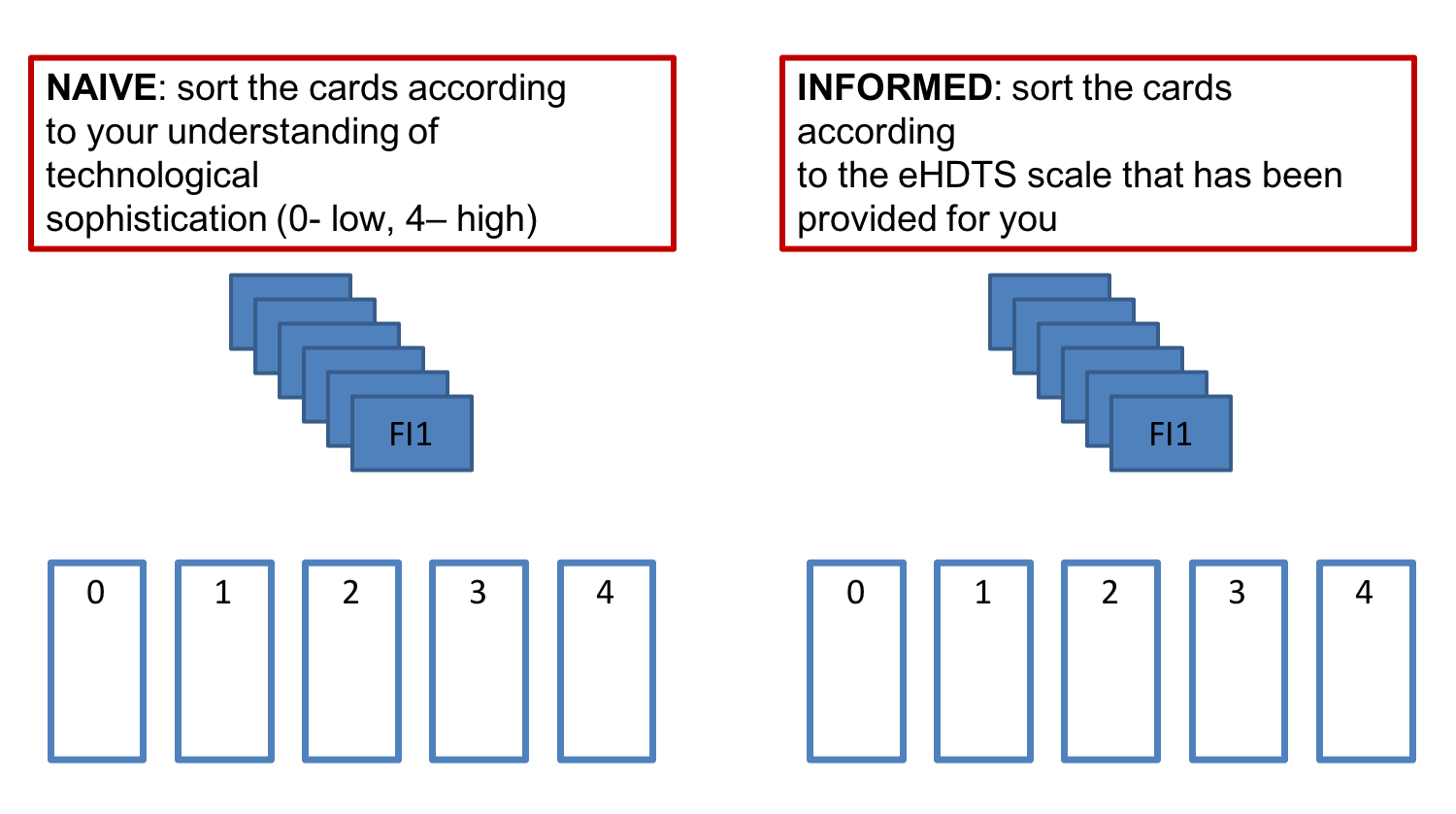
To assess concurrent validity of the eHDTS scale, coders were asked to sort function instantiations (snippets of text describing functions) into five "buckets" of increasing technological sophistication according to their own understanding of "technological sophistication." Two weeks later they were asked to do this task again but then the buckets were labeled according to the levels of the eHDTS scale. All coders had technical backgrounds.
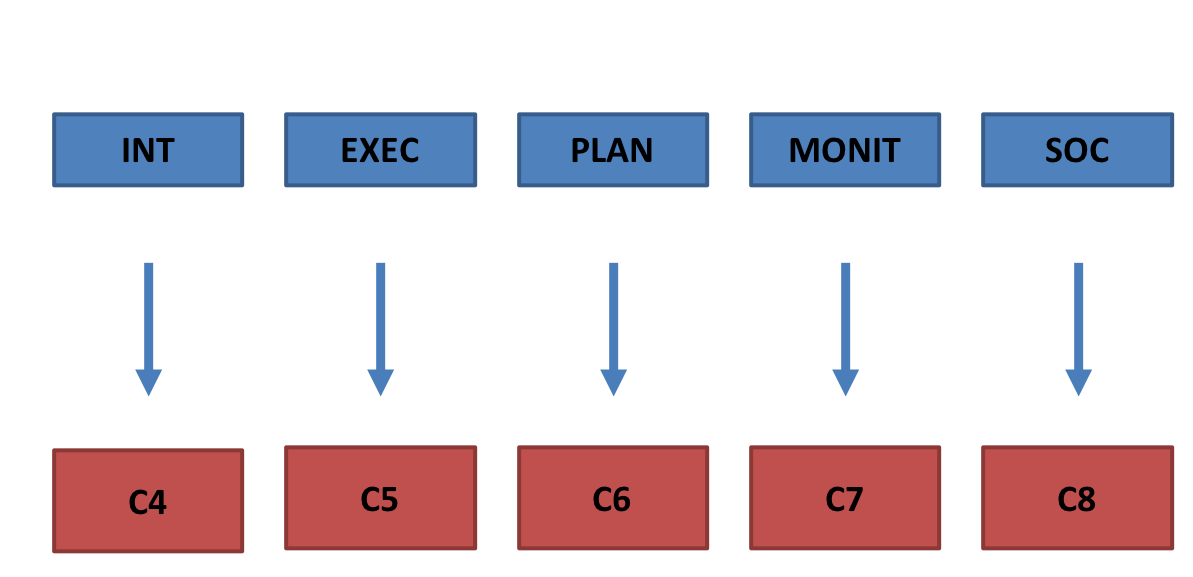
The eHDTS scales are five different scales with slightly different level definitions according to the function type that a scale is intended for. To determine whether the scales are comparable, a coder was given functions from all different types mixed and asked to rate them according to his understanding of technological sophistication. Two weeks later, the type of function was revealed and the coder was again asked to rate the function with the corresponding eHDTS scale.